News/ The 19th China Ecology Conference·Sustainable Ecological Design Sub-forum was successfully held
The 19th China Ecology Conference·Sustainable Ecological Design Sub-forum was successfully held
2020-12-02 15:10 
Sponsored by the Chinese Society of Ecology and undertaken by the South China Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the "19th China Ecology Conference" was successfully held online on November 21-23, 2020. The theme of the conference was "New Mission of Ecological Science: Promoting the Harmony of Man and Nature ". Invited by the organizing committee of the conference, the School of Design of Shanghai Jiaotong University is responsible for the preparation and organization of the "Sustainable Ecological Design" sub-forum.
On the afternoon of November 21, the "Sustainable Ecological Design" sub-forum was successfully held online. From Tsinghua University, Peking University, Shanghai Jiaotong University, Tongji University, Dalian University of Technology, Chongqing University, Guangxi University, Shanghai University of Technology, Nanjing University of Technology and other famous domestic universities, Shanghai Academy of Landscape Planning, Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences Nearly a hundred experts and scholars in sustainable ecological design related fields such as the Institute for Sustainable Development, the Fraunhofer Institute-IBP Institute for Building Flow in Germany and other domestic and foreign research institutes, as well as the Environmental Design Institute of Huajian Group and other related fields of sustainable ecological design gathered online for exchanges Share cutting-edge research and viewpoints on sustainable ecological design.
The first half of the forum was chaired by Professor Che Shengquan, Vice Dean of the School of Design.
Zhang Lang, dean of Shanghai Academy of Landscape Planning and Research and a professor-level senior engineer, gave a report entitled "Ecological Space Identification and Ecological Landscaping of Potential Green Spaces in Urban High-density Areas". With the rapid development of urbanization and the gradual optimization of the layout of urban space functions, the scarcity of land resources has become an important restrictive factor in the construction of urban ecological environment. For example, Shanghai’s requirement of “negative growth in the scale of planned construction land” requires more and more "City difficult sites" carry out landscaping activities. He gave the concept and classification of "Challenging Urban Sites" (Challenging Urban Sites). The ecological garden construction method of urban difficult sites is a comprehensive application of urban ecology, environmental science, afforestation and gardening, and systems engineering and other disciplines and techniques to carry out the spatial transformation and functional enhancement of urban difficult sites. Taking Shanghai's central city area (within the outer ring line) as the key research area, the analysis results show that the proportion of urban difficult sites in the approved and unplanned green space is 74%, and the urban difficulties in the parks and green spaces that have been built in 2009-2018 Sites (urban relocation sites) accounted for more than 80%, up to 91.4%, and the overall trend is increasing. On the basis of the overall distribution of potential green space in Shanghai, corresponding restoration measures and actual cases were given for three typical difficult sites of urban relocation, three-dimensional greening, and landfill.

Professor Wang Yuncai, deputy director of the Department of Landscape Studies, School of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tongji University, reported on "the construction of an ecological space priority system based on multiple ecosystem service levels". He pointed out that in urbanized areas with limited natural space, it is of great significance to identify natural spaces with key ecological functions based on the comprehensive capabilities of ecosystem services, and to build effective and efficient ecological networks on this basis. They surveyed by ecosystem service experts, determined the five key ecosystem service measurements and maps provided by the natural space in the Sujia Lake area, and built a coupled ESs evaluation model for multiple ecosystem services in the ecological space. The multi-ecosystem service level of the space and river corridors is evaluated. Based on the evaluation of the single ecosystem, the multi-ecosystem service capability index (MESC index) of each natural space is calculated through the evaluation of the multi-ecosystem service coupling. The level of MESC index carries out cluster analysis and priority system evaluation and division of ecological space. The index evaluation results show that in the two types of natural spaces, lakes and forests, the overall level of ESs supply is the highest. The result of cluster analysis shows that the natural space priority can be divided into six levels. The method he proposed based on the evaluation of MESC indicators is a newly constructed system model of ecological space priority evaluation, which can effectively express the service capacity and level of the ecological space and the spatiality of the ecological system, and is useful for the identification and identification of important natural spaces in landscape ecological network planning. Management provides a scientific and repeatable framework, and provides useful reference information for planners and decision makers.

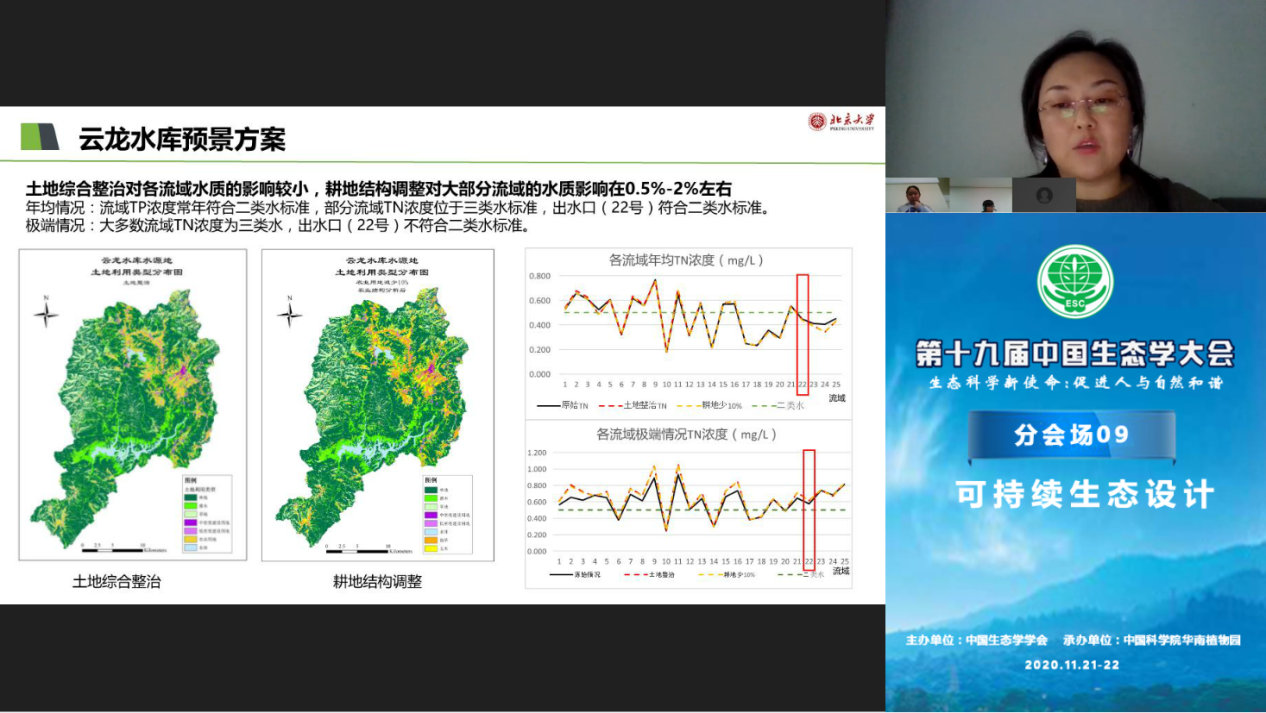
The report of Wang Zhifang, an associate professor of the School of Architecture and Landscape Design of Peking University, focused on "Sustainable Ecological Design Strategies for Water Source Protection Areas". China has designated strict water source protection areas and is classified as an ecological red line, but most of the existing water source protection areas cannot truly realize the sustainable development of water source areas. She took Baimei Reservoir in Fuzhou City of Fujian Province and Yunlong Reservoir in Kunming City of Yunnan Province as examples to explore sustainable ecological design and management strategies for water sources. The study uses dynamic simulation of the human-land-water changes within the water source area, and further divides the management and control of the water source area into strict control areas, ecological restoration areas, risk control areas and restricted development areas, and formulates corresponding ecological design strategies. The management and control of water sources will promote the sustainable development of water sources. Research has strong innovative and practical significance for the pollution process, water quality prevention and control, and the effective implementation of water source control.
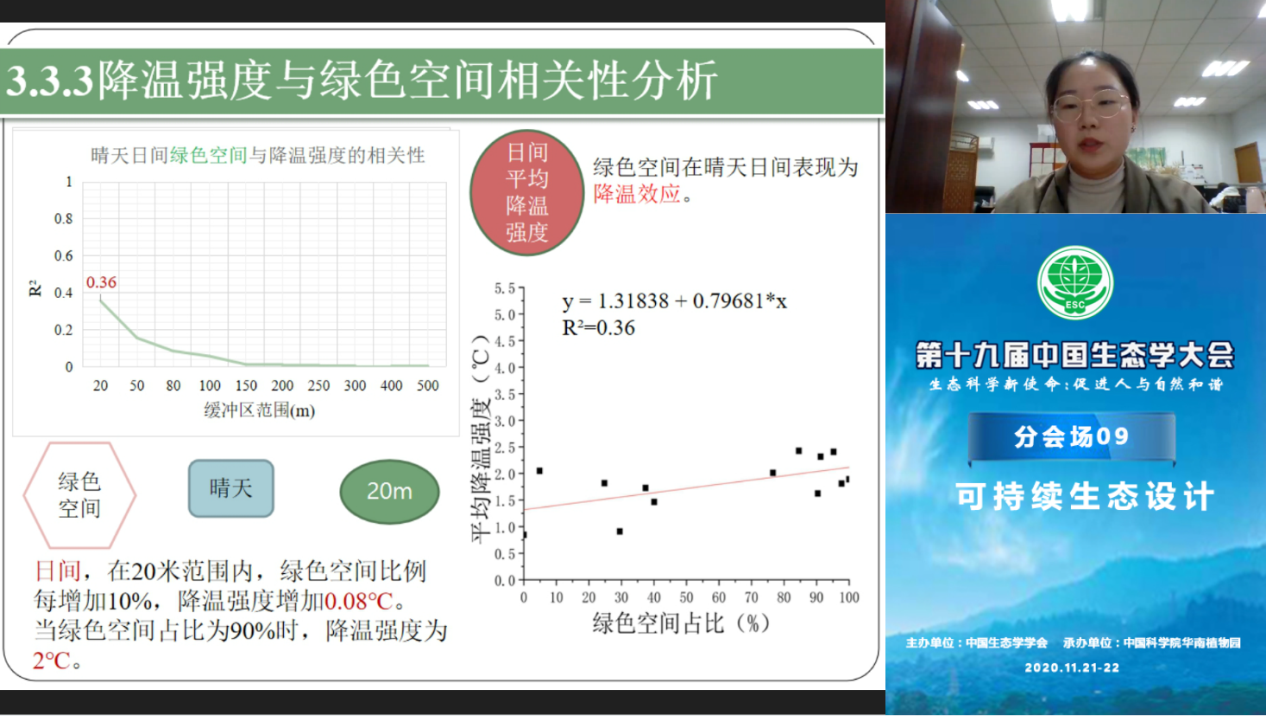
Professor Cai Yongli, deputy director of the Sustainable Ecological Design Center of the School of Design, Shanghai Jiaotong University, and his postdoctoral fellow, Wang Wei, shared the "Research on Shanghai Urban Heat Island Effect". In recent years, in the economically developed coastal cities, a large number of urban renewal measures have been used to alleviate urban heat islands, including increasing vegetation coverage and closing high-energy-consuming factories. So can these urban renewal measures effectively improve the urban climate? The results of their research are positive. Using Shanghai's 144 years of meteorological observation data and high-resolution urban land use, anthropogenic heat and other information, an effective UHI assessment method has been established. They chose Xujiahui Station as the city station and Fengxian Station as the suburban station. They calculated that UHI increased first and then decreased from 1990 to 2016. UHI decreased by about 0.58 °C from 2005 to 2016, which was due to the effective Urban renewal measures are mainly the increase in vegetation coverage within the city and the closure of a large number of high-energy-consuming factories. Further numerical simulation studies have also proved that in the future urban scenarios, increasing vegetation by 10-20% in the form of roof greening and street parks can reduce UHI 0.38-0.78°C, which corresponds to saving electricity of 3.05-5.79×108 kWh/year and Reduce carbon emissions by 2.47-4.68×105 tCO2/year. This research will help us to improve the urban climate through urban renewal in the process of large-scale urbanization, and help us better understand the impact of changes in the underlying environment of the city on the urban climate, so as to formulate reasonable measures to reduce UHI and promote the city Sustainable development of the ecological environment.

Du Hongyu, an assistant researcher at the Institute of Ecology and Sustainable Development of the Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences, gave a report titled: Research on Urban "Blue and Green Space" Landscape Planning Strategies Based on the Cold Island Effect-Taking Shanghai as an example. The report pointed out that mitigating the urban heat island effect is a scientific and social issue that needs to be solved urgently, and the urban "blue-green space" has a significant cold island effect. According to the simulation results of CFD technology, the order of different forms of green land cold island effect from strong to weak is: wedge shape>radial shape>band shape>point shape. The order of the urban "blue-green space" on the improvement of human comfort from strong to weak is: LSI large lake>LSI small lake>planar green space>point green space>river>band green space. Urban water landscape planning strategies: (1) Integrate the water ecosystem; (2) Control the development intensity of urban construction land around the river; (3) Increase landscapes such as artificial lakes and ponds. Urban green space landscape planning strategies: (1) Optimize the planning and layout of Shanghai’s green space system; (2) Pay attention to the expansion of heat islands in suburban urban centers as early as possible; (3) Establish a greening management and supervision mechanism for private spaces. The overall planning strategy for the city’s “blue-green space”: (1) Create a “cold zone” on the main internal roads and ring roads in the city to increase the city’s air permeability; (2) Add “cold spots” in the central city to “ The "cold spots" break up the heat island area; (3) Protect and increase the "cold surface" outside the central city to maximize the cold island effect. The results can provide a basic reference for my country to formulate relevant regulations to reduce the heat island effect.

The second half of the forum was hosted by Professor Cai Yongli of the School of Design.
The first speaker in the second half was Li Hong, a senior researcher at the Fraunhofer Institute-IBP Institute of Building Flow in Germany, and executive director of the Fraunhofer Project Center of Shanghai Jiaotong University at FPC. He focused on "urban design in the era of smart interconnection" share it. He believes that design no longer only cares about shape, color and space, but more and more turn to science, rigor, implementability and controllability. The report starts with the exploration of data applications in urban design, based on the digital twin concept pioneered by Fraunhofer in Germany, and puts forward the concept of seeking ecologically sustainable solutions from the conception stage of urban design to the deepening implementation stage with smart data analysis methods. Combining specific cases in Shanghai’s Hongqiao core area, Chongming Eco-Island, Xiongan New District, Essen Duisburg, Germany, etc., discuss the precise use of data in urban design, the use of evolutionary methods, and the perspective of urban design from urban spatial clusters The distribution relationship between clusters and ecological space clusters, the functional distribution logic of urban space, start with urban energy utilization, urban traffic operation and other aspects, study the evolution law of urban spatial structure and form, and propose a novel urban design methodology.

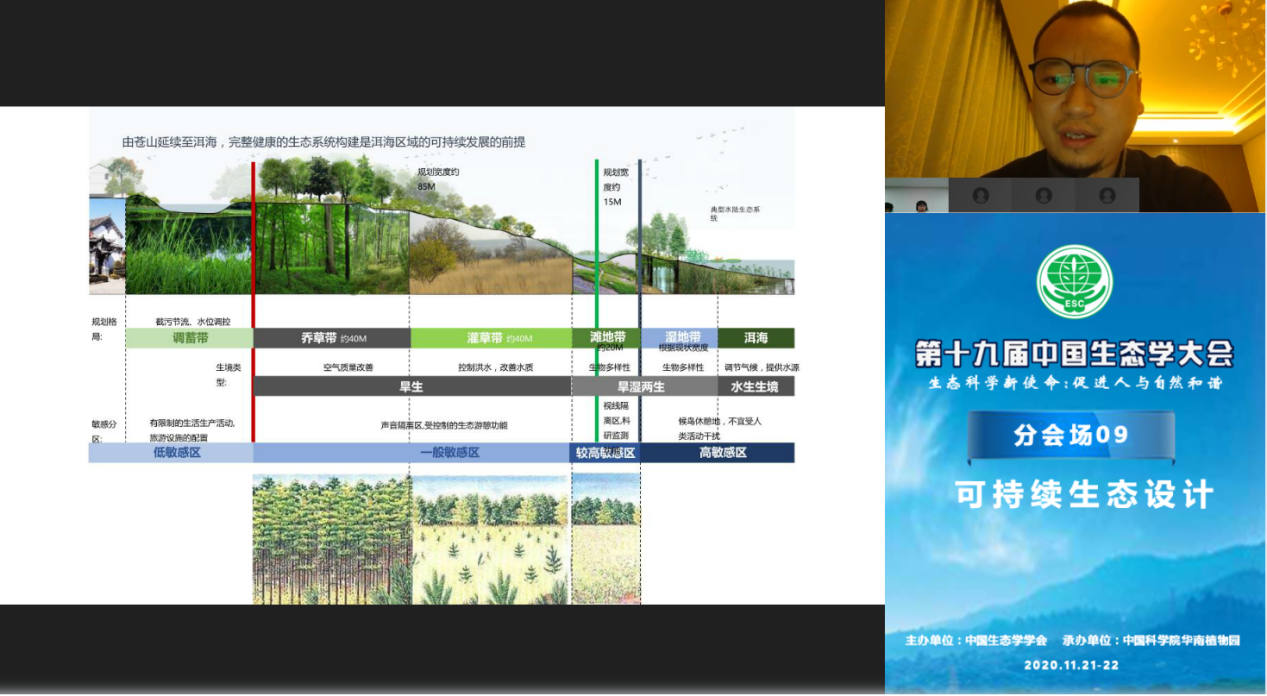
Yang Lingchen, Deputy Dean of the Landscape Design Institute and Director of the Third Landscape Design Institute of Huajian Group Environmental Institute (Shanghai Modern Building Decoration Environmental Design Research Institute Co., Ltd.), focuses on the “lakeside buffer zone ecological restoration and landscape design practice with water quality protection as the core ——Taking the construction project of the Erhai Lake Ecological Corridor in Dali as an example", a systematic introduction to the ecological restoration and wetland construction projects of the Erhai Lake buffer zone. This project is different from the conventional waterfront landscape project. As one of the national ecological challenges, this design preparation is summarized into five key issues: how to establish a complete Cangshan and Erhai ecosystem, and how to use the lakeside buffer zone to physically isolate the Erhai Lake. How to use the lakeside buffer zone as the last barrier for ecological protection of the Erhai Lake, how to restore the ecological corridor environment, and how to solve the problem of water quality in the ditches into the lake. In response to the actual problems faced, the design team proposed a "protection +" strategy. Through the implementation of wetland construction projects, ecological restoration projects, and lakeshore base restoration, under the premise of ensuring the quality of Erhai Lake, through the construction of ecological patterns, ecologically sensitive areas Division, construction of low-impact development rainwater system and establishment of ecological monitoring operation system to complete the protection of the ecological environment of Erhai Lake, and through the injection of humanistic connotation, the reshaping of functional style, the linkage of regional industries and the driving of urban development, Pursuing to shape the harmonious development of man and nature, creating a "world-class plateau lake characteristic ecological corridor" integrating ecology, style, humanity and management.
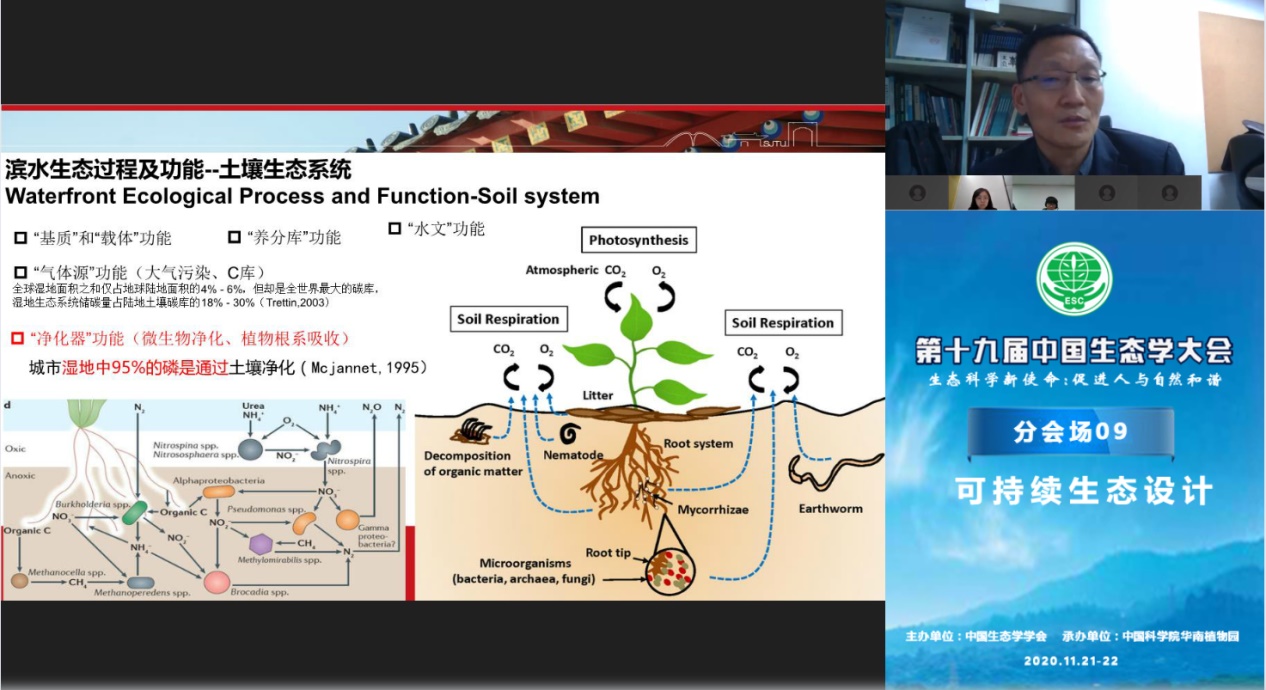
Che Shengquan gave a report entitled "Ecological Design and Ecological Restoration of Urban Waterfront Space". He first analyzed the relationship between mankind and nature, and pointed out that the bottom line of ecology is that man's use of nature does not exceed nature's ability to regulate. From the perspective of ecological design, science and philosophy are combined, and human beings are part of the ecosystem. Ecological aesthetics is the philosophical basis for the realization of ecological design; ecological governance emphasizes source reduction, process control, and end restoration. The structure and function of the urban waterfront ecosystem are described. The regulation function of the microclimate is one of the ecological service functions of the waterfront ecological space; the waterfront ecological process is closely related to the soil ecosystem, and the waterfront slope protection can retain and purify pollutants to reduce runoff pollution and maintain water quality safety. Maintain the stable function of the waterfront space ecosystem. In terms of case application, in the integrated area of the Yangtze River Delta, the ecological function evaluation and ecological design countermeasures of the Dianshan Lake waterfront area were studied, and the targeted enhancement design of the ecological service function in the blue pearl chain area was done. Both cases Organically integrate ecological philosophy, ecological aesthetics and ecological technology, and combine rural revitalization with cultural conservation.
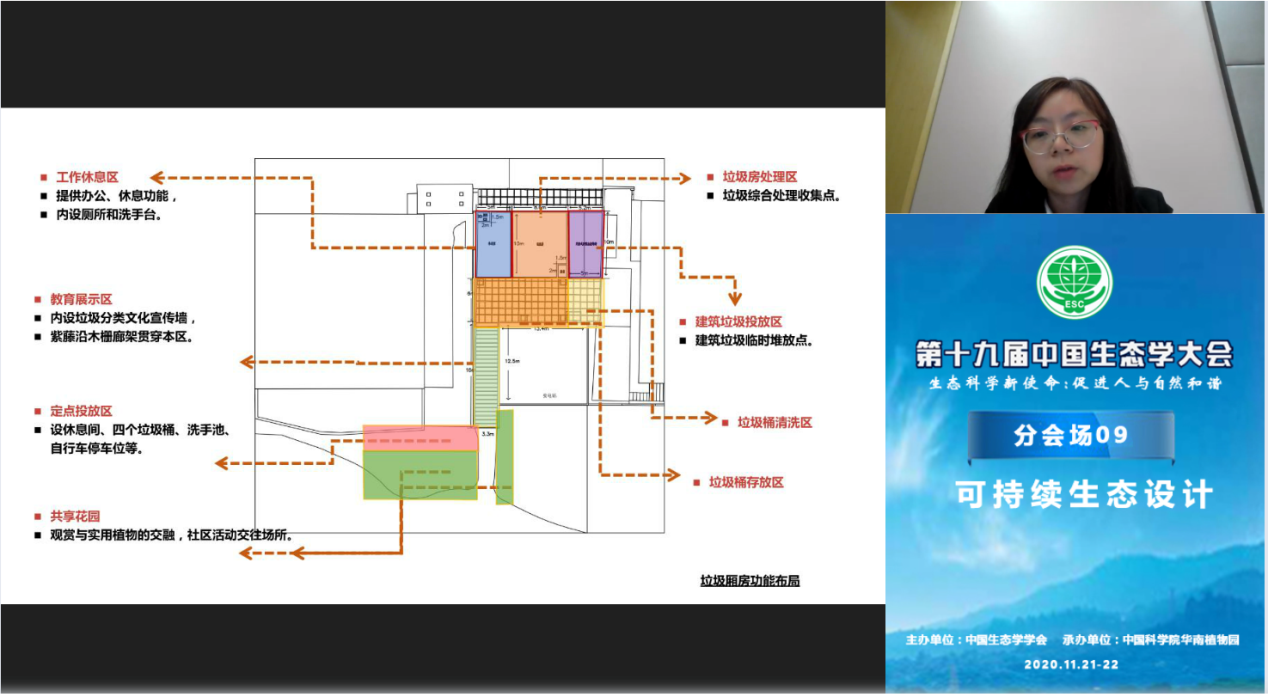
Gou Aiping, a professor at the School of Eco-Technology and Engineering at Shanghai University of Applied Sciences, focused on "Research and Practice on the Reconstruction of Garbage Wings under the Background of the Integration of Two Networks-Taking Shanghai as an Example". First, combined with the experience and technology of actual projects at home and abroad, explored The matching design method and strategy introduces the realization of the deep integration and connection of the "domestic waste removal network" and the "renewable resource recovery network". The research group took the practice of several different types of garbage wing renovation projects hosted by Shanghai Jing’an District as an example. Based on the analysis of the original garbage wing’s problems in cleaning and transportation, dust, noise, classification, and disposal, it fully considered the health and housing of residents. The inherent needs of the environment, starting from the perspectives of spatial layout, clean transportation flow, mute noise reduction, dust reduction and odor reduction, etc., propose four aspects of functional integration, waste reduction, safe transportation, ecological maintenance, and quiet operation The transformation strategy.
"Research on the optimization of high-density built environment based on bird's acoustic landscape perception enhancement-Taking Chongqing Nan'an District as an example" by Li He, a doctoral student in the Urban and Rural Planning Department of Chongqing University She studied the high-density built-up area of Chongqing Nan'an District as an example, combined with the intuitive perception and perception needs of urban residents to investigate the current situation of the bird acoustic landscape characteristics in the high-density built environment, and the activities of urban birds in the high-density built environment Behavior analysis and simulation of the corresponding ecological flow process path, combined with the spatial distribution characteristics of the ecological space in the high-density built environment, the actual construction and operation conditions, the survival needs of birds and the landscape needs of residents, analyze the current high-density built environment of birds The current characteristics of the acoustic landscape, explore the urban spatial factors that affect the bird acoustic landscape, explore how to improve the bird acoustic landscape perception in the high-density built environment, and propose a combination of multiple needs for the bird acoustic landscape bearing space in the high-density built environment Optimize the path, and explore the promotion and optimization strategy from the two-way dimensions of space and time.

Feng Ningye, a graduate student of the Green Building and Eco-City Laboratory of the School of Architecture, Nanjing University of Technology, introduced their research results around "Research on the Thermal Environment Characteristics and Climate Adaptability Design Strategy of Urban Waterfront Parks". The research results show that the overall cooling effect of the waterfront park is very significant. Compared with the urban center, the daily maximum temperature of Xuanwu Lake Park and Green Expo Park can be reduced by 3.1-4.3℃ and 4-5.7℃, respectively. Compared with water bodies, the cooling effect of green space is more significant, and the temperature drop with vegetation is about 2.8℃ higher than that without vegetation. Urban waters have limited mitigation effects on surrounding heat islands, and increasing vegetation coverage in the waterfront can greatly increase the cooling intensity. When designing the internal space of the park, it is necessary to combine the “blue and green” system and pay attention to the local area. The influence of the microclimate.
This forum brought together experts, scholars and practitioners in related fields at home and abroad to exchange and discuss the existing research results and practical experience of ecological design from different perspectives, which played a positive role in promoting the construction and development of sustainable ecological design disciplines.
The China Ecology Conference is a branded academic event organized by the Chinese Ecological Society, and it is also the most influential, largest and most authoritative academic event in the domestic ecology community. Nearly 40 years have passed since the first Ecology Conference was held in 1979. Its main academic exchange activities include conference theme reports, special sub-venue reports, academic posters and other forms. The Chinese Ecology Conference aims to carry out ecological exchanges and cooperation more extensively and effectively, calling on ecological workers to pay attention to ecological civilization, maintain ecological safety, realize sustainable development, jointly promote ecological development and social harmony and progress, and protect our common life Promote the construction of ecological civilization, realize the green mountains and green waters, and fulfill the responsibility of a great country.


 Tel 021-34206578 021-54742134
Tel 021-34206578 021-54742134 SCHOOL OF DESIGN, SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY,NO.800 DONGCHUAN ROAD,MINHANG DISTRICT,SHANGHAI.
SCHOOL OF DESIGN, SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY,NO.800 DONGCHUAN ROAD,MINHANG DISTRICT,SHANGHAI. Email 200240
Email 200240